A good XML sitemap acts as a roadmap for your website, guiding Google to all your important pages.
XML sitemaps are also beneficial for SEO because they allow Google to quickly find your key web pages, even if your internal linking is not perfect.
What are XML sitemaps?
You want Google to crawl every page of your website, but sometimes pages exist on the server without any internal links pointing to them, making it difficult for bots to discover them.
An XML sitemap lists the important pages of a website, allowing Google to find and crawl them all and helping Google understand the structure of your website.
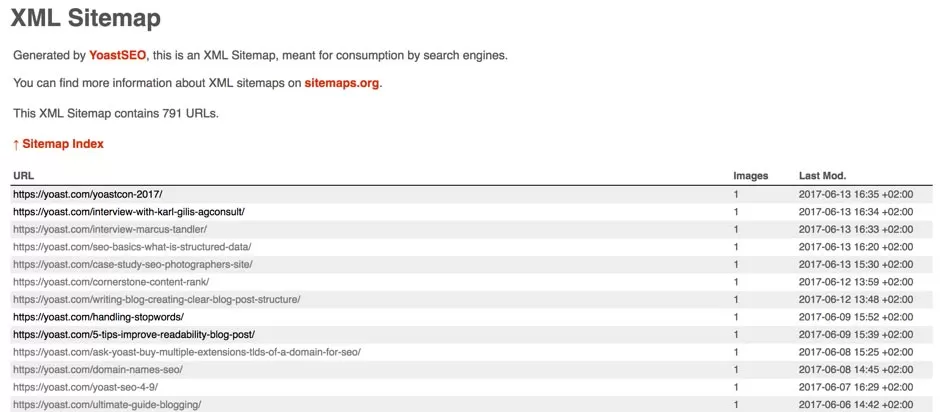
Above is Yoast.com’s XML sitemap generated by the Yoast SEO plugin. Later in the article, we will explain how the plugin can help you create the best XML sitemaps. If you’re not using this plugin, your sitemap might look a bit different, but it will function in the same way.
As you can see, the Yoast.com XML sitemap displays several ‘index’ sitemaps: post-sitemap.xml, page-sitemap.xml, video-sitemap.xml, and so on. This categorization makes the structure of a site as clear as possible. When you click on one of the index sitemaps, you will see all the URLs in that sitemap. For example, if you click on the post-sitemap.xml link, you will see all Yoast.com’s post URLs
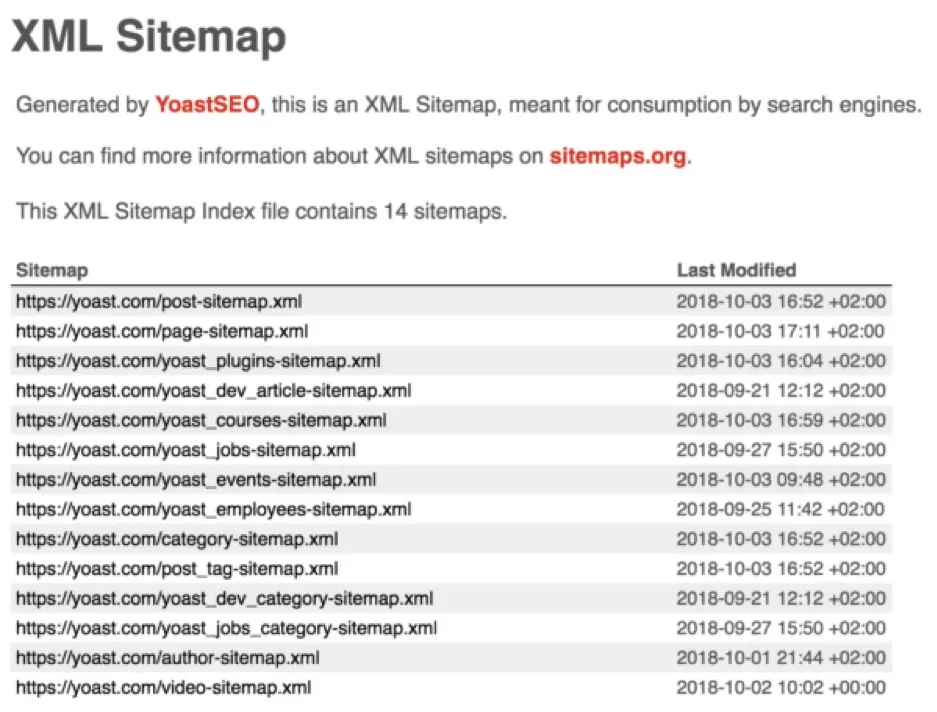
At the end of each line you will see a date. This tells Google when each post was last updated. When a date changes in the XML sitemap, Google knows that there is new content to be crawled and indexed.
If you have a very large website, sometimes you need to allocate an index sitemap. A single XML sitemap is limited to 50,000 URLs, so if your website has more than 50,000 posts, you’ll need two separate addresses for the URLs, effectively adding a second index sitemap.
Which websites need an XML sitemap?
Google’s documentation states that XML sitemaps are useful for “really large websites,” “websites with extensive archives,” “new websites with only a few external links,” and “websites that use rich media content.”
What pages should be in your XML sitemap?
When deciding which pages to include in your XML sitemap, start by considering the relevance of the URLs.
If you don’t want a URL to appear in search results, you need to add a ‘noindex, follow’ tag. Removing it from your XML sitemap does not mean that Google will not index the URL. If Google can find a page by following links, it can index the URL.
How to get Google to find your sitemap
If you want Google to find your XML sitemap faster, you need to add it to your Google Search Console account. In the ‘Sitemaps’ section, you will immediately see if your XML sitemap has already been added. If not, you can add your sitemap to the top of the page.
Check your own XML sitemap!
Now that you have read the whole article carefully, it’s your turn. Now that you understand how important it is to have an XML sitemap and how it can truly help your site’s SEO, it’s not hard to see that it’s a matter that really deserves careful attention.
If you add the right URLs, Google can easily access your most important pages and posts. Google will also be able to easily find updated content, so it will know when to re-crawl a URL. Finally, adding your XML sitemap to Google Search Console helps Google quickly find your sitemap and allows you to check for any sitemap errors.
Now you can check your own XML sitemap and ensure that it is done correctly!