Domain Authority (DA) is a search engine ranking score developed by Moz that predicts how well a website will perform in search engine results pages (SERPs). A Domain Authority score is a value ranging from 1 to 100 that corresponds to a website’s potential for higher search engine rankings.
Domain Authority is calculated by evaluating multiple factors, including root domains and total number of links, into a single DA score. This score can then be used to compare websites or track a website’s “ranking power” over time. Domain Authority is not a metric used by Google to determine search rankings and does not impact SERPs.
You can view a website’s DA using MozBar (a free Chrome extension), Link Explorer (a backlink analysis tool), the SERP Analysis section of Keyword Explorer, and many other SEO tools available on the web.
How is Domain Authority calculated?
Domain Authority is scored on a logarithmic scale from 1 to 100. Thus, increasing your score from 20 to 30 is much easier than increasing it from 70 to 80.
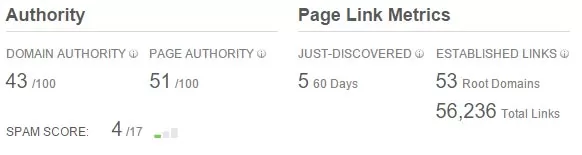
What is a "good" Domain Authority?
Generally speaking, sites with a large number of high-quality external links (such as Wikipedia or Google.com) are at the top of the Domain Authority scale, whereas smaller businesses and websites with fewer links may have a lower DA. New websites always start with a Domain Authority score of zero.
Since Domain Authority is a predictor of a site’s ability to rank, getting a very high DA score should not be your only goal. Look at the DA scores of sites you directly compete with in SERPs and aim to achieve a higher score than your competitors. It is best used as a comparative metric (rather than an absolute, concrete score) when searching search results and determining which sites may have stronger / more important link profiles than others. Since this is a comparative tool, there is no such thing as a “good” or “bad” Domain Authority score.
Domain Authority (DA) vs. Page Authority (PA)
Domain Authority measures the predicted ranking strength of entire domains or subdomains, while Page Authority measures the strength of individual pages.
Technical definition of Domain Authority
Domain Authority is based on data from our Link Explorer web directory and uses dozens of factors in its calculations. The actual Domain Authority calculation uses a machine learning model to find the “best” predictive algorithm, closely related to our link data and thousands of real search result rankings that we use as standards for scaling.
Because the Authority relies on machine learning calculations, your site’s score will often fluctuate as more, fewer or different data points are used in the calculation; for example, if Facebook gets billions of new links, everyone’s KA and DA will drop in relative terms. So keep in mind that you should always use Domain Authority as a relative metric to compare with other sites’ link profiles, as opposed to an absolute value that scores the effectiveness of your internal SEO efforts.
How do I influence Domain Authority?
Domain Authority is difficult to influence directly. It is the sum of a metric that has an impact on the authority score and linkage data. This metric means how competitive a particular site is in Google search results. Since Google considers many factors, a metric that tries to calculate it must also include many factors.
The best way to influence the Domain Authority metric is to improve your overall SEO. Specifically, you should focus on your link profile by acquiring more links from other well-linked pages.
Why has my authority changed?
Because Domain Authority (and, therefore, Page Authority) is made up of multiple metrics and calculations, it can be difficult to pinpoint the exact cause of a change. If your score has increased or decreased, there are many potential influencing factors, such as
- Your link profile growth has not yet been captured in the web directory.
- The highest authority regions have shown remarkable growth, distorting the scaling process.
- You have earned links from places that do not contribute to Google rankings.
- Your linked domains were crawled more or less than before.
- Your Domain Authority is at the lower end of the scoring spectrum and is therefore more affected by scaling volatility.

